Cingal® for healthcare
professionals
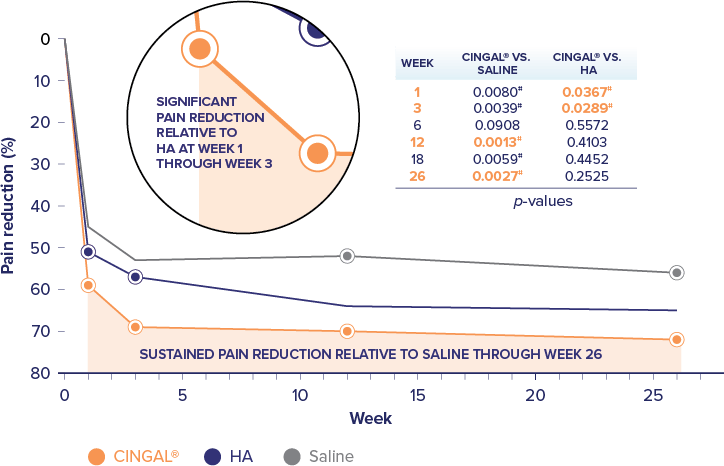
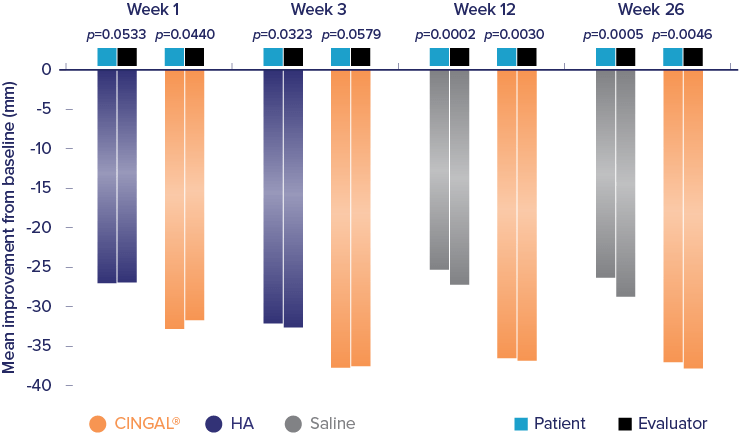
Cingal® (hyaluronic acid and triamcinolone hexacetonide) is indicated for the treatment of pain in osteoarthritis (OA) of the knee in patients who have failed to respond adequately to conservative non-pharmacologic therapy and to simple analgesics (e.g., acetaminophen). Cingal® includes an ancillary steroid to provide additional short-term pain relief.1